How Does an Arc Welding Machine Work?
Introduction
Arc welding is one of the most common and dependable metal-joining processes used in Nigeria’s construction, fabrication, and manufacturing industries. Whether you’re working in a workshop, shipyard, or construction site, an arc welding machine is a must-have for joining metals with precision and strength.
In simple terms, arc welding uses electricity to create heat, which melts and fuses two metal parts together. Once the molten metal cools, it forms a strong joint that can withstand heavy loads, pressure, and vibration. This makes arc welding a favorite in automotive repair, structural steelwork, and industrial maintenance.
At GZ Industrial Supplies, we provide high-quality welding machines and consumables that meet professional standards ensuring durability, performance, and safety for every welder.
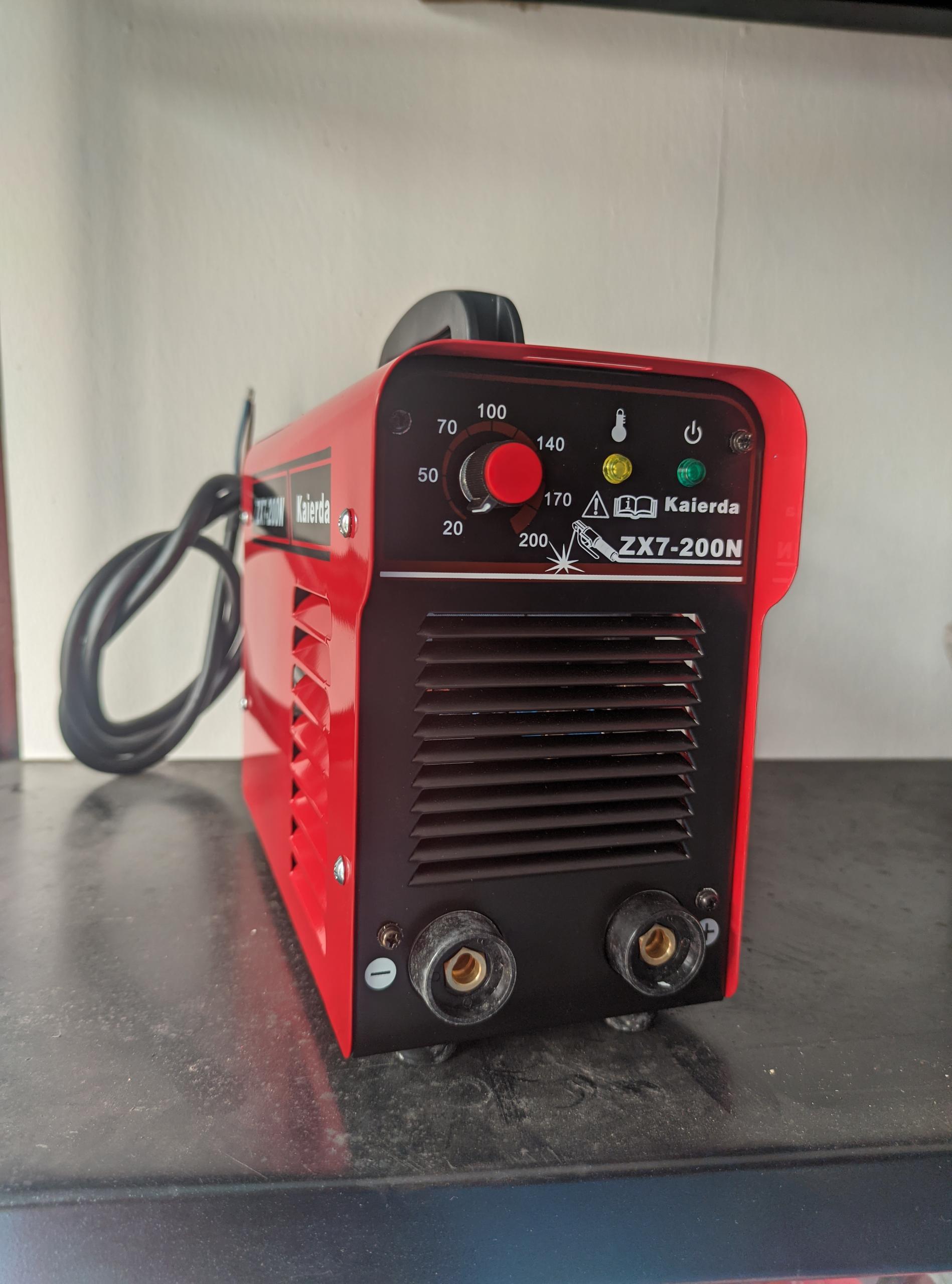
Kaierda Inverter/Arc Welding machine ZX7-200N/220V/DC
What Is Arc Welding?
Arc welding is a process that joins metals using an electric arc, a continuous discharge of electricity between the electrode and the metal workpiece. The intense heat generated (up to 6,000°C) melts the edges of the metal, allowing them to fuse together upon cooling.
There are different types of arc welding processes, but the core principle remains the same using an electrical current (either AC or DC) to melt the metals and form a strong bond.
Arc welding is often preferred because it:
- Produces strong, lasting joints.
- Works effectively on thick metals.
- Is portable and affordable for workshops and field jobs.
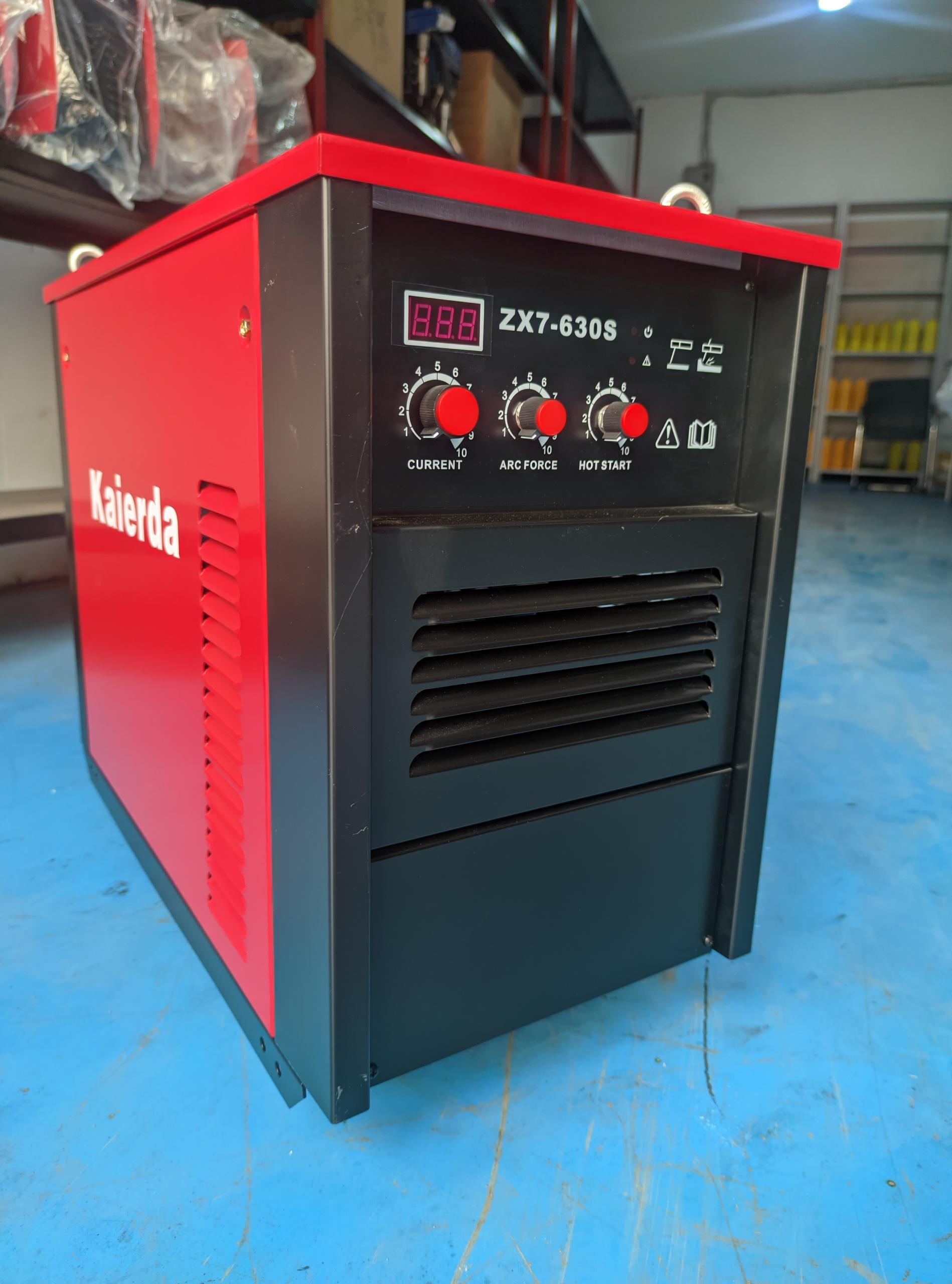
Kaierda Inverter Manual Arc Welding Machine (ZX7-630S)
Main Components of an Arc Welding Machine
To understand how arc welding works, it’s important to know the main parts that make up the machine:
- Power Source:
This supplies the electric current. It can be AC (Alternating Current) or DC (Direct Current) depending on the welding type and materials. - Electrode Holder:
Holds the electrode (the metal rod that carries current) and allows the welder to control its movement during welding. - Electrode:
Acts as both the conductor and filler material. When the arc forms, the electrode melts and fills the joint. - Ground Clamp:
Connects the workpiece to the machine to complete the electrical circuit. - Cables & Connectors:
Carry current from the power source to the electrode and back through the ground clamp. - Cooling System (in industrial models):
Keeps the machine from overheating during continuous welding. - Protective Gear:
Essential for safety includes gloves, apron, helmet with auto-darkening filter, and protective clothing.
Step-by-Step: How an Arc Welding Machine Works
Here’s a simple breakdown of how the welding process happens:
- Setup:
Connect the power source, ground clamp, and electrode holder securely. Ensure safety gear is in place. - Arc Formation:
The welder strikes the electrode lightly against the metal surface, this creates an electric arc that produces intense heat. - Melting Process:
The heat melts both the electrode tip and the metal edges, forming a molten pool. - Fusion:
As the electrode feeds into the molten area, it adds filler material, joining the two metal parts together. - Cooling and Solidification:
When the arc is stopped, the molten metal cools and solidifies into a strong welded joint.
Types of Arc Welding Processes (SMAW, MIG, TIG, etc.)
There are several types of arc welding processes, each suited to different applications, materials, and working conditions. At GZ Industrial Supplies, we supply machines and accessories for all major arc welding methods used across Nigeria’s construction, marine, and industrial sectors.
Let’s explore the most common types:
Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW)
Also known as Manual Metal Arc (MMA) or Stick Welding, this is the most widely used type in Nigeria. It uses a consumable coated electrode that melts to form the weld. The coating produces a shielding gas and slag that protect the molten pool from contamination.
Advantages:
- Simple, portable, and affordable.
- Works well for both outdoor and indoor environments.
- Perfect for structural steel, gates, pipelines, and heavy equipment repairs.
Ideal For:
Construction sites, shipyards, fabrication workshops, and field repairs.
Metal Inert Gas Welding (MIG)
Also called Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), this process uses a continuous wire electrode and an external shielding gas (usually argon or CO₂). It’s faster and cleaner than SMAW, producing neat welds with minimal slag.
Advantages:
- High productivity with fast weld speeds.
- Smooth and clean finish, perfect for visible joints.
- Easier for beginners due to automatic wire feed.
Ideal For:
Automotive bodywork, metal furniture, light fabrication, and indoor projects.
Tungsten Inert Gas Welding (TIG)
Known technically as Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW), this process uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode with a separate filler rod. It offers precise control over the weld pool, making it ideal for thin materials and decorative work.
Advantages:
- Produces the cleanest and strongest welds.
- Ideal for stainless steel, aluminum, and non-ferrous metals.
- No spatter or smoke, excellent for high-end fabrication.
Ideal For:
Aerospace, food-grade steel tanks, exhaust systems, and aluminum fabrication.
Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW)
A semi-automatic process similar to MIG, but the wire has a flux core that eliminates the need for an external shielding gas. It’s suitable for outdoor environments where wind could blow away the gas shield.
Advantages:
- Excellent for thick materials and outdoor welding.
- High deposition rate and strong weld penetration.
- Performs well in construction and heavy equipment repair.
Ideal For:
Outdoor fabrication, shipbuilding, and industrial manufacturing.
Submerged Arc Welding (SAW)
Used mainly in large-scale industrial applications, SAW involves feeding a continuous electrode beneath a blanket of granular flux. The arc remains hidden (submerged), which minimizes spatter and increases weld quality.
Advantages:
- High efficiency and deep penetration.
- Minimal smoke and heat loss.
- Suitable for thick plates and large joints.
Ideal For:
Pipeline manufacturing, pressure vessels, and structural beams.
Quick Comparison Table: Arc Welding Methods
|
Welding Type |
Electrode Type |
Shielding Method |
Typical Use |
Skill Level |
|
SMAW (Stick) |
Consumable coated rod |
Flux coating |
Heavy-duty outdoor & field repairs |
Easy |
|
MIG |
Continuous wire |
External gas (Argon/CO₂) |
Automotive & fabrication |
Beginner |
|
TIG |
Tungsten electrode |
Inert gas |
Stainless steel, aluminum |
Advanced |
|
FCAW |
Flux-cored wire |
Internal flux |
Outdoor, construction |
Moderate |
|
SAW |
Continuous wire |
Granular flux |
Industrial, pipelines |
Professional |
Advantages of Arc Welding
Arc welding remains one of the most versatile and affordable metal joining methods in the world—and for good reason. Whether you’re a professional fabricator or an apprentice in Nigeria’s growing manufacturing sector, understanding its benefits can help you choose the right machine.
Strength and Durability
Weld joints created by arc welding are extremely strong and can handle heavy loads, vibration, and stress.
Versatility
Arc welders work on various metals including mild steel, stainless steel, and cast iron.
Portability
Compact inverter arc welding machines are lightweight and perfect for on-site work, making them a top choice for Nigerian welders.
Cost-Effectiveness
Compared to MIG or TIG, stick welding equipment is more affordable and requires less setup.
Availability of Electrodes
SMAW electrodes like E6013 and E7018 are widely available across Nigerian industrial markets, including GZ Industrial Supplies branches and distributors nationwide.
Common Challenges and Safety Precautions in Arc Welding
While arc welding is one of the most efficient and powerful methods of joining metals, it also requires precision, care, and strict safety practices. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or a new welder, understanding the common challenges and safety precautions will protect you, your equipment, and your work quality.
Welding Spatter
Tiny droplets of molten metal, known as spatter, can scatter during welding, leaving rough surfaces or burns on nearby materials.
Solution:
Adjust current and voltage settings properly. Use anti-spatter spray or gel, and maintain a steady electrode distance.
Porosity (Gas Bubbles in Welds)
Porosity happens when gas becomes trapped in the molten weld pool, creating weak spots or holes.
Solution:
Ensure surfaces are clean before welding, use quality electrodes, and avoid moisture on the workpiece or rods.
Cracks or Incomplete Fusion
Cracks or poor bonding occur when heat input is too low or the arc isn’t steady enough.
Solution:
Maintain correct current levels and electrode angles, preheat thicker metals, and fill gaps properly.
Overheating or Burn-Through
Too much current or staying in one spot too long can burn holes through thin metal.
Solution:
Reduce amperage, move smoothly, and use electrodes suited for thinner materials like E6013.
Slag Inclusion
Slag (the protective layer formed during welding) can get trapped in the weld if not cleaned between passes.
Solution:
Chip and brush the weld after every pass to remove slag, and maintain proper welding speed and angles.
Safety Precautions in Arc Welding
Arc welding produces extreme heat, bright light, and fumes that can be dangerous without proper protection. Below are essential precautions every welder in Nigeria should follow:
Always Wear Protective Gear
Invest in a welding helmet with an auto-darkening filter, flame-resistant gloves, long sleeves, and boots. Never weld with bare skin exposed—the ultraviolet (UV) light can cause severe burns.
Ensure Good Ventilation
Welding fumes contain gases and particles that can harm your lungs. Always weld in an open or well-ventilated area. Use fume extractors for confined spaces.
Check Equipment Regularly
Inspect cables, clamps, and connectors for wear or frayed insulation. Faulty cables can cause electric shocks or short circuits.
Handle Electrodes Safely
Keep electrodes dry and store them in airtight containers to prevent moisture absorption, which can cause porosity in welds.
Avoid Flammable Areas
Never weld near fuel, oil, or gas containers. Keep fire extinguishers and sand buckets nearby at all times.
Protect Others
Install welding screens or barriers to shield nearby workers from arc flashes. Even brief exposure to the arc can cause eye injuries.
Disconnect Power After Use
Always turn off and unplug your welding machine when not in use to avoid accidental electrical discharge or short circuits.
Applications of Arc Welding in Nigeria
Arc welding plays a major role in Nigeria’s industrial growth, powering key sectors that rely on strong and efficient metal joining techniques. Some of the most prominent industries include:
Construction and Infrastructure
From bridges and pipelines to residential and commercial buildings, arc welding is essential for creating durable steel frameworks. Structural beams, columns, and reinforcements depend on high-quality welds that can withstand environmental stress.
GZ Industrial Supplies supports this industry by supplying heavy-duty SMAW and MIG welders, welding rods, and protective equipment for field and workshop use.
Oil & Gas Industry
Nigeria’s oil and gas sector uses arc welding extensively in pipeline fabrication, refinery maintenance, and offshore rig structures. The harsh working conditions demand equipment with consistent performance and reliability.
GZ Industrial Supplies provides industrial-grade inverter welding machines and accessories that meet international standards for offshore and onshore welding.
Automotive and Transportation
In car repair workshops and manufacturing plants, arc welding helps in frame repair, chassis fabrication, and exhaust assembly. It’s ideal for both mild and stainless steel applications.
GZ Industrial Supplies ensures mechanics and auto engineers have access to compact yet powerful Dongcheng, Maxmech, and Enegyz welding machines, designed for precision work.
Marine and Shipbuilding
Welding is a cornerstone of shipbuilding and marine repair in coastal regions like Lagos, Port Harcourt, and Warri. Arc welding creates watertight joints and repairs hulls, decks, and engine components.
GZ Industrial Supplies supplies corrosion-resistant electrodes and marine-grade welding consumables to support marine engineers and dockyards.
Manufacturing and Fabrication Workshops
From furniture makers to industrial equipment manufacturers, arc welding is used daily to build metal frames, machinery, gates, tanks, and storage systems.
GZ Industrial Supplies offers all-inclusive welding setups; machines, filler rods, helmets, and spares — helping workshops maintain continuous production with minimal downtime.
GZ Industrial Supplies’s Role in Empowering Nigerian Welders
At GZ Industrial Supplies, our mission is to empower welders, engineers, and manufacturers with reliable tools and training to achieve professional results.
We achieve this by providing:
Top-Quality Welding Machines: From SMAW to TIG, we stock the most trusted brands in Nigeria.
Safety Equipment: Helmets, gloves, aprons, and eyewear that meet international standards.
Technical Support: Expert guidance on machine setup, maintenance, and choosing the right accessories.
Nationwide Delivery: Supplying welders across Nigeria — from Lagos to Abuja, Kano, and Port Harcourt.
Industries GZ Industrial Supplies Actively Supports
|
Sector |
Welding Application |
GZ Industrial Supplies Solutions |
|
Construction |
Steel frames, beams, supports |
SMAW machines, E6013 electrodes |
|
Oil & Gas |
Pipelines, rigs, tanks |
Industrial inverter welders |
|
Automotive |
Body repair, chassis work |
Compact MIG & TIG welders |
|
Manufacturing |
Machinery, fabrication |
Multiprocess welders, safety kits |
|
Marine |
Hulls, docks, vessels |
Corrosion-resistant consumables |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What type of arc welding machine is best for beginners?
For beginners, the SMAW (Stick) welder is the best starting point. It’s affordable, portable, and versatile. Models like the Dongcheng MMA inverter welder available at GZ Industrial Supplies are ideal for learning and small fabrication tasks.
2. Can I use an arc welding machine for aluminum or stainless steel?
Yes, but the type of metal determines the process. TIG welders are best for aluminum and stainless steel due to their precision and clean welds, while MIG or Stick welders are better for carbon steel and thicker materials.
3. How much power does an arc welding machine need?
Most arc welding machines operate between 160A–400A and require either a single-phase (220V) or three-phase (415V) power source, depending on the model and use case. Portable models for home and workshop use can run on standard power.
4. Why does my arc keep sticking to the metal?
This usually happens when the amperage is too low or the electrode angle is incorrect. Adjust your current settings and keep a steady arc gap of about 2–3 mm to maintain smooth operation.
5. Where can I buy quality arc welding machines and accessories in Nigeria?
You can purchase authentic and affordable arc welding machines, electrodes, helmets, and safety gear directly from GZ Industrial Supplies — trusted nationwide for industrial and construction welding equipment.
Conclusion
Arc welding remains one of the most essential skills in Nigeria’s manufacturing, construction, and repair industries. Whether you’re welding pipelines, automotive parts, or steel structures, understanding how your arc welding machine works helps you achieve better performance and safer results.
At GZ Industrial Supplies we go beyond selling machines, we provide training, technical support, and the right accessories to ensure every welder performs with confidence and precision.
From inverter welders to safety gear GZ Industrial Supplies has you covered.
Shop online or visit any of our branches to discover durable and affordable welding machines that deliver consistent results.
Contact us:
Email:sales@gz-supplies.com
Phone: +234-533-901-29
Website: https://www.gz-supplies.com/