How to Troubleshoot and Maintain Water Pumps for Industrial Use
Introduction
Water pumps are the lifeblood of many industrial operations powering essential processes in manufacturing plants, construction sites, refineries, and water treatment facilities. Their role in transferring liquids, regulating pressure, and maintaining system flow makes them indispensable across sectors.
Yet, even the most robust pump systems can suffer from unexpected breakdowns if not properly maintained. Issues like cavitation, seal leakage, or overheating often lead to costly downtime, reduced efficiency, and expensive repairs.
This comprehensive guide is designed to help industrial technicians, engineers, and facility managers troubleshoot common pump problems and implement proactive maintenance practices. Whether you're managing a single unit or overseeing a large pump network, the insights here will help extend equipment lifespan, reduce unplanned stoppages, and keep your operations running smoothly.
Common Water Pump Problems in Industrial Settings
Cavitation
- What it is: formation of air bubbles that cause shockwaves
- Symptoms: rattling noise, reduced efficiency, vibration
- Cause: improper suction head or blockage
Seal and Gasket Leaks
- What it is: fluid leakage from pump housing
- Symptoms: dripping, loss of pressure
- Causes: worn seals, overpressure, improper installation
Overheating
- What it is: excessive rise in temperature during operation
- Symptoms: pump shuts down, high surface temperature
- Causes: blocked flow, running dry, failed bearings
Excessive Vibration
- What it is: abnormal movement leading to wear
- Causes: misalignment, loose mounting, imbalance
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Guide
Check Power Supply
- Ensure consistent voltage
- Test fuses, breakers, and connection terminals
Inspect for Leaks
- Visual checks on seals, pipes, and casings
- Use pressure tests to detect internal leaks
Evaluate Suction and Discharge Conditions
- Confirm suction line is clear of obstructions
- Ensure correct pressure at discharge valve
Listen for Abnormal Noises
- Use sound patterns to detect cavitation or bearing failure
Measure Flow Rate and Pressure
- Compare with manufacturer specs
- Identify drops in performance
Routine Maintenance Best Practices
Scheduled Inspections
- Weekly visual checks
- Monthly system performance review
- Quarterly oil and seal inspection
Lubrication
- Use manufacturer-recommended oils
- Avoid over-lubrication
Alignment Checks
- Ensure motor and pump shafts are perfectly aligned
Seal Replacement
- Replace seals periodically even before failure
- Use original manufacturer parts
Cleaning and Flushing
- Clean suction strainers and impellers
- Flush out sludge and debris quarterly
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Guide
Inspect Power Supply and Connections
Check if the pump is receiving power. Inspect for blown fuses, tripped breakers, or faulty wiring.
Check the Suction Line and Inlet Filter
Clogs or blockages in the inlet or suction line can reduce performance. Clean or replace filters as needed.
Examine the Pump Casing and Impeller
Inspect for cracks, wear, or buildup of debris. A worn impeller can drastically reduce water flow.
Monitor Pump Bearings and Seals
Worn bearings create noise and vibration. Leaking seals can lead to contamination or inefficiency.
Evaluate System Pressure and Flow Rate
Use pressure gauges and flow meters to assess whether the pump is operating within its design parameters.
Review Operating Conditions
Overheating, cavitation, or dry running are signs of improper installation or load mismatches.
Routine Maintenance Checklist
Regular maintenance prevents costly downtime and extends the life of your industrial water pump. Here's a checklist to follow weekly, monthly, and quarterly:
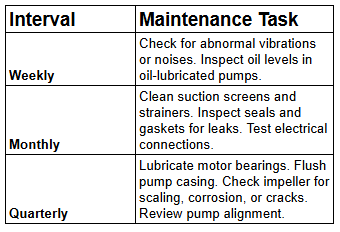
Tip: Always refer to the manufacturer’s maintenance manual for specific guidelines tailored to your pump model.
Best Practices for Long-Term Pump Health
To get the most out of your industrial water pumps, implement these long-term strategies:
Use the Right Pump for the Job
Match flow rate, pressure, and fluid type with the pump’s specifications. Undersized pumps lead to strain; oversized pumps waste energy.
Install Surge Protection Devices
Especially for electrically driven pumps, to prevent damage from voltage spikes.
Implement Vibration Monitoring Systems
This predictive maintenance tool alerts you to bearing wear, misalignment, and motor faults early.
Ensure Proper Ventilation and Cooling
Overheating shortens motor life. Keep surrounding areas clean and well-ventilated.
Train Staff on Correct Operation
Many failures stem from improper use. Regular training ensures safe and efficient operations.
Common Replacement Parts and When to Replace Them
Over time, certain components of industrial water pumps wear out due to constant use. Replacing them on time ensures reliability and safety.
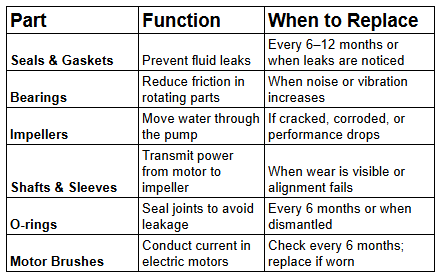
Pro Tip: Stock commonly needed spare parts for your specific pump models to minimize downtime.
When to Call a Professional vs DIY Fixes
While some issues can be handled in-house, others require the attention of certified technicians.
DIY Maintenance Tasks
- Checking oil levels and topping up
- Cleaning filters and strainers
- Tightening bolts and fittings
- Flushing debris from pump casing
- Replacing simple components like O-rings
Call a Professional For
- Electrical motor rewinding or failure
- Shaft misalignment and vibration analysis
- Repeated seal/gasket failure
- Pressure or flow inconsistencies after maintenance
- Overheating without an obvious cause
Tips: If a problem persists after two rounds of DIY troubleshooting, it’s time to bring in an expert.
Safety Tips for Handling and Servicing Water Pumps
Whether performing routine maintenance or emergency repairs, safety should always come first when working with industrial water pumps.
General Safety Precautions
- Turn Off Power Supply: Always disconnect the pump from its power source before inspection or service.
- Lockout/Tagout (LOTO): Follow proper lockout procedures to prevent accidental startup.
- Release Pressure: Depressurize the system before opening flanges or valves.
- Wear PPE: Use gloves, safety goggles, and steel-toe boots during handling.
- Check for Leaks or Corrosives: Be aware of chemical residues and fluids that may cause burns or slips.
Fire and Electrical Safety
- Keep electrical components dry and protected from moisture.
- Never attempt repairs on wiring without proper insulation tools and training.
- Store flammable cleaning agents away from the pump room.
Smart Practices
- Keep a first aid kit and emergency shut-off plan nearby.
- Train all maintenance staff on pump-specific procedures.
- Maintain a clear logbook of repairs and inspections.
Frequently asked Questions
1. What are the most common problems with industrial water pumps?
Learn about issues like cavitation, seal failure, overheating, and low pressure.
2. How can I tell if my industrial water pump is failing?
Warning signs include strange noises, reduced flow, vibration, leaks, and erratic performance.
3. What routine maintenance should be done on a water pump?
Regular inspections, lubrication, seal checks, alignment, and cleaning of filters are essential.
4. How often should an industrial water pump be serviced?
It depends on usage, but typically every 3–6 months for preventive maintenance is recommended.
5. What tools are needed for pump troubleshooting and maintenance?
Common tools include vibration analyzers, pressure gauges, thermal cameras, alignment tools, and wrench sets.
Conclusion
Maintaining industrial water pumps isn’t just about preventing failure, it’s about ensuring continuous operations, saving costs, and protecting equipment longevity. From regular inspection schedules and understanding pump performance to identifying parts that need replacement, a proactive maintenance plan makes all the difference.
Looking to equip your facility with durable water pumps or schedule a professional inspection?
Visit GZ-Supplies.com or Tikweld.com today for high-quality industrial pumps, accessories, and expert support.
Have questions or need technical assistance?
Email: sales@gz-supplies.com or chat with us on WhatsApp.







